Access to clean, safe water is a critical issue facing many communities around the world. With water being a limited resource, especially in arid regions, finding innovative solutions for water harvesting is essential. While local bodies of water have traditionally been the primary source of water, researchers are now exploring new ways to extract moisture from the air to generate potable water.
Earth’s atmosphere contains trillions of liters of fresh water vapor, but collecting this colorless and dilute gas is a significant challenge. Previous systems that focused on trapping dew or fog were not effective in dry areas that lack sufficient moisture. To address this issue, researchers have been developing absorbent materials like temperature-responsive hydrogels, metal-organic frameworks, and zeolites to pull moisture from the air and release it when heated.
A Novel Approach to Water Harvesting
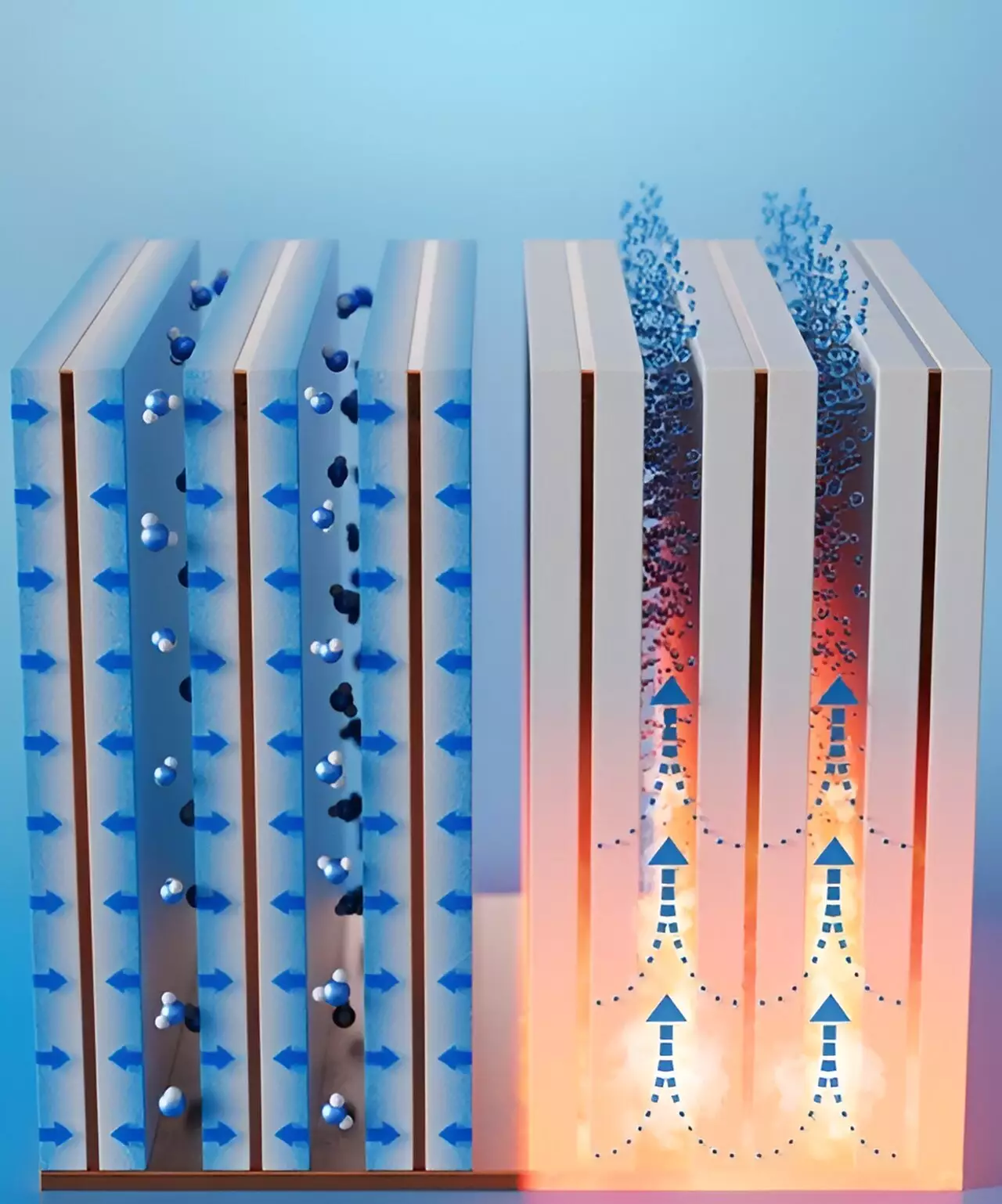
In a recent study published in ACS Energy Letters, Xiangyu Li, Bachir El Fil, and their team introduced a novel humidity harvester that aims to revolutionize water harvesting in arid regions. The researchers designed water-adsorbent “fins” coated with zeolite to efficiently trap moisture from the air. Unlike previous studies that focused solely on material development, this research emphasized the co-design of the adsorption bed with material properties to create thin, compact, and highly efficient adsorbent fins.
The prototype device featured 10 small adsorbent fins placed on a copper base plate, strategically spaced to maximize moisture capture from desert-like air. Once the fins reached saturation, the trapped moisture was released when the base plate was heated to 363 Fahrenheit. Through 24 collection-release cycles, the researchers estimated that 1 liter of absorbent coating on the fins could produce up to 1.3 liters of potable water per day in air with 30% relative humidity, significantly outperforming previous devices.
Future Applications and Implications
This innovative water harvesting system presents a promising opportunity for rapid moisture capture multiple times per day. The researchers envision integrating this technology into existing infrastructures that produce waste heat, such as buildings or transportation vehicles, to provide a cost-effective and sustainable solution for generating potable water in arid regions. With continued development and refinement, the potential for this system to address water scarcity in dry areas is significant.
The development of compact and portable water harvesting devices like the one created by Xiangyu Li, Bachir El Fil, and their team represents a crucial step towards ensuring access to clean water in arid regions. By harnessing the power of technology and innovative materials, we have the opportunity to transform the way we harvest water and address the pressing challenges of water scarcity.

Leave a Reply