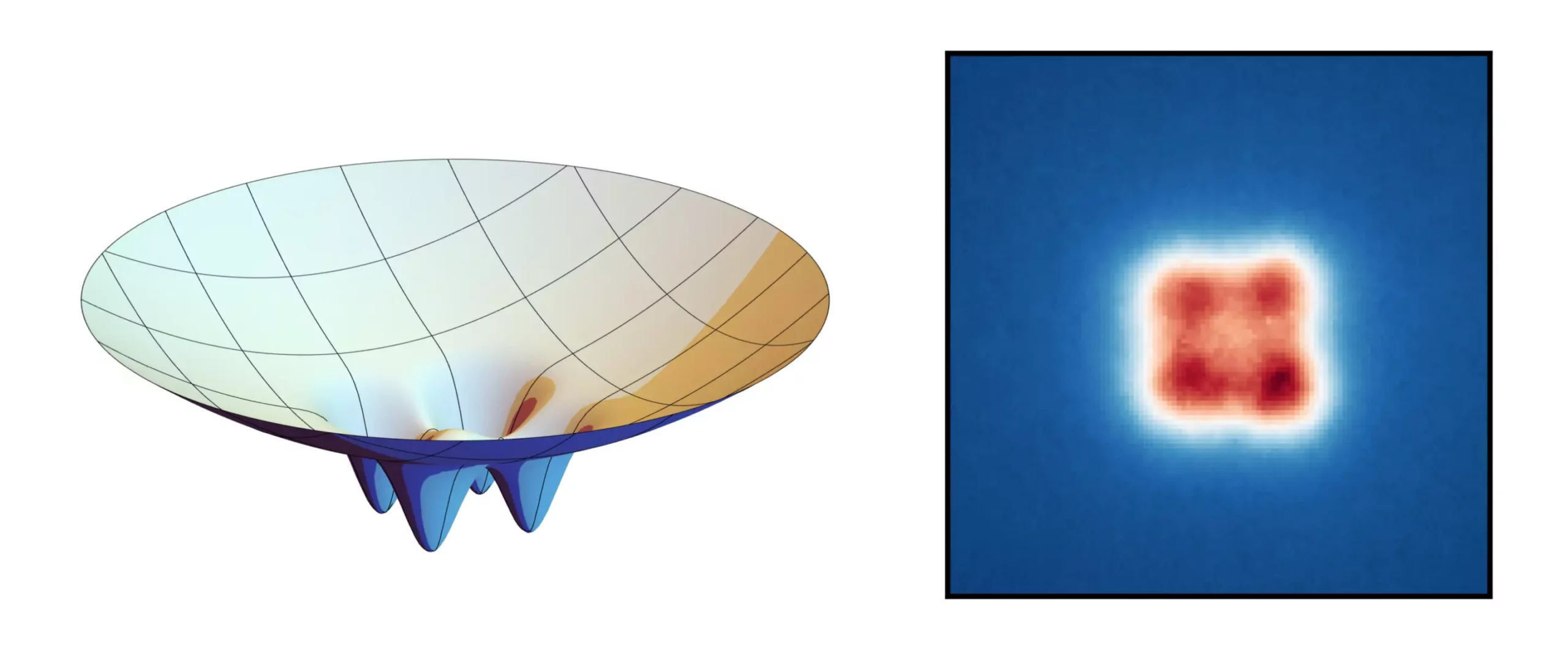
In a groundbreaking study conducted by researchers at the University of Bonn, it has been discovered that thousands of light particles can combine to form a unique entity known as a “super photon” under specific circumstances. By utilizing small nano molds, scientists have been able to manipulate the structure of this Bose-Einstein condensate, effectively shaping the speck of light into a simple lattice consisting of four points arranged in a quadratic form.
The process involves cooling a large number of light particles to an extremely low temperature and confining them within a compact space. This results in the particles becoming indistinguishable and acting as a single super photon. Typically, a Bose-Einstein condensate appears as a hazy speck of light, but with the recent development, researchers have successfully imprinted a lattice structure onto the condensate.
The implications of this discovery are significant, particularly in the realm of secure communication. The structured condensate could potentially be utilized to facilitate tap-proof information exchange among multiple participants. The concept of quantum entanglement, where a change in one particle affects another instantaneously, could be harnessed to ensure secure discussions and transactions.
By deliberately altering the reflective surfaces, researchers believe that it is feasible to create Bose-Einstein condensates divided into numerous lattice sites, ranging from 20 to 30 or even more. This advancement opens up possibilities for enhancing communication security in group settings, paving the way for innovative applications in various fields.
The research conducted at the University of Bonn represents a significant step forward in the field of quantum physics. By manipulating light particles to form super photons with specific structures, scientists have demonstrated the potential for secure information exchange through quantum entanglement. This achievement lays the groundwork for further exploration and application of quantum phenomena in various technological advances.

Leave a Reply