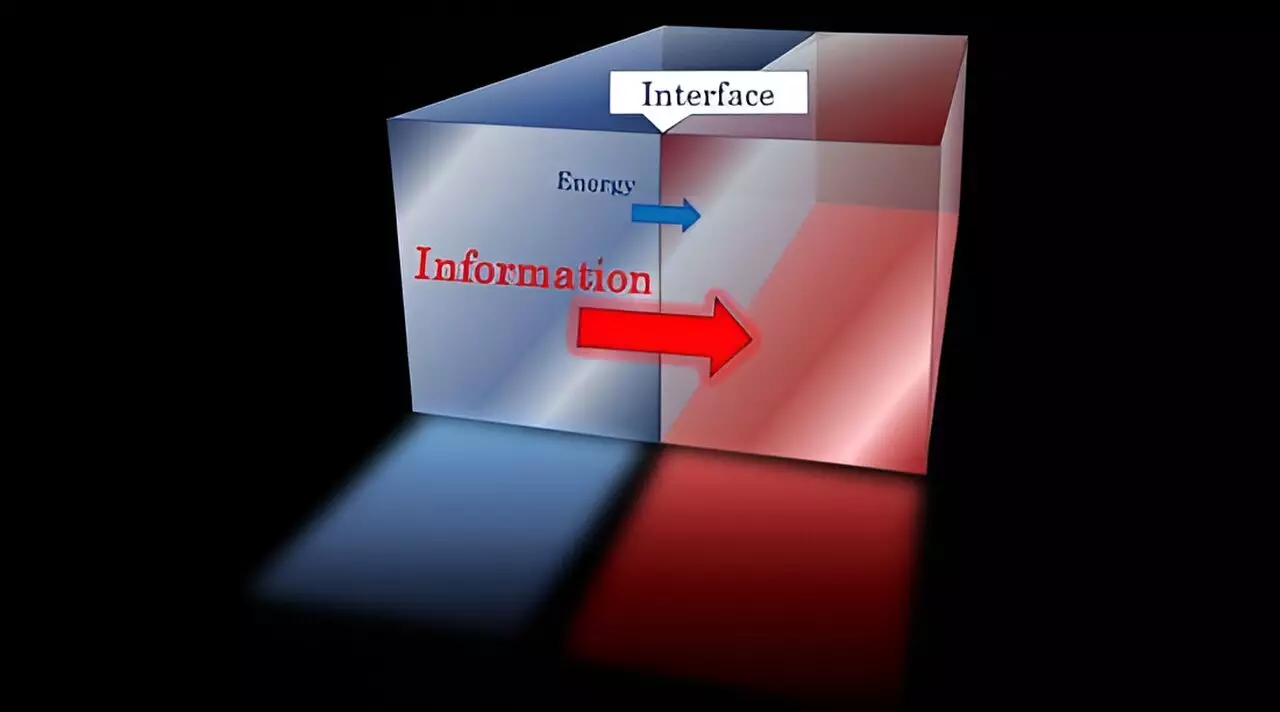
In a groundbreaking study published in *Physical Review Letters*, an international consortium of researchers unveiled a deceptively straightforward relationship governing the rates at which energy and information are transmitted across quantum field theory interfaces. This revelation, led by noted physicists Hirosi Ooguri from the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe and Fred Kavli from Caltech, presents a significant advance in our understanding of two-dimensional quantum systems characterized by scale invariance. The interface—the boundary between different quantum field theories—has long posed a complex challenge for physicists. Traditionally, calculating energy and information transfer rates across such boundaries has been a daunting task; thus, this breakthrough offers not only clarity but also opens avenues for further exploration in both particle physics and condensed matter physics.
Understanding the Inequalities
The researchers articulated a set of universal inequalities that intricately link three essential quantities: the energy transmission rate, the information transmission rate, and the size of the Hilbert space, which indicates the proliferation of states at high energy. The key inequalities presented are:
1. Energy Transmittance ≤ Information Transmittance
2. Information Transmittance ≤ Size of the Hilbert Space.
At first glance, these relationships may appear mathematical in nature, yet their implications resonate on multiple levels. They suggest a foundational principle: any effective mechanism for transmitting energy necessitates the transmission of information, and that both processes hinge upon the existence of a sufficiently rich set of states. Moreover, the assertion that no stronger inequalities can be established elevates these findings, signaling a critical advancement in the theoretical underpinnings of quantum mechanics.
The Implications for Quantum Mechanics
The implications of this research extend far beyond theoretical physics. By elucidating the intrinsic link between energy and information transfer, the study emboldens future research aimed at manipulating these parameters for practical applications. Potential areas for innovation include quantum computing, where the seamless transfer of information is paramount, and energy dynamics in condensed matter systems where understanding fundamental interactions can lead to technological breakthroughs. Furthermore, this understanding can influence the development of quantum materials and devices that uphold these principles, ultimately contributing to advancements in quantum technology.
Why This Research Matters
This research elevates the importance of interfaces in quantum field theories from mere mathematical abstractions to crucial elements that govern the core dynamics of various physical systems. By making the complex relationship between energy and information more comprehensible, the findings represent a unifying theory that could pave the way for new models and simulations in quantum mechanics. In a field often marred by intricate calculations and theoretical obscurity, Ooguri and Kavli’s team has illuminated a path through complexity. The insights gleaned from this study underscore the necessity for a deeper understanding of fundamental physics relationships, propelling researchers towards more comprehensive explorations of the quantum realm.
Through these revelations, the study not only deepens theoretical comprehension but also enhances the potential for upcoming technologies reliant on these quantum principles, ultimately propelling society into an era where the dictates of quantum mechanics may become operationalized to effect real-world change.

Leave a Reply