The realm of robotics has long been informed by the pursuit of creating machines that can mimic human capabilities. A recent breakthrough from a research team at the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics is set to redefine our understanding of robotic touch. By skillfully merging traditional internal force-torque sensors with advanced machine-learning techniques, the team has developed a novel method of touch sensing that circumvents the need for artificial skin. This innovative approach captures the essence of tactile interaction that we, as humans, experience daily.
The Two-Way Nature of Touch
In living organisms, the sense of touch operates on a reciprocal basis. When one object comes into contact with another, both parties engage in a complex exchange of information that includes texture, pressure, and even temperature. Historically, designing robots to experience a comparable form of touch was a significant challenge due to the limitations of existing technologies. However, this new research highlights a paradigm shift, as it recognizes that touch can be perceived through internal mechanical signals rather than relying solely on external sensing mechanisms.
Emulating Human Sensitivity
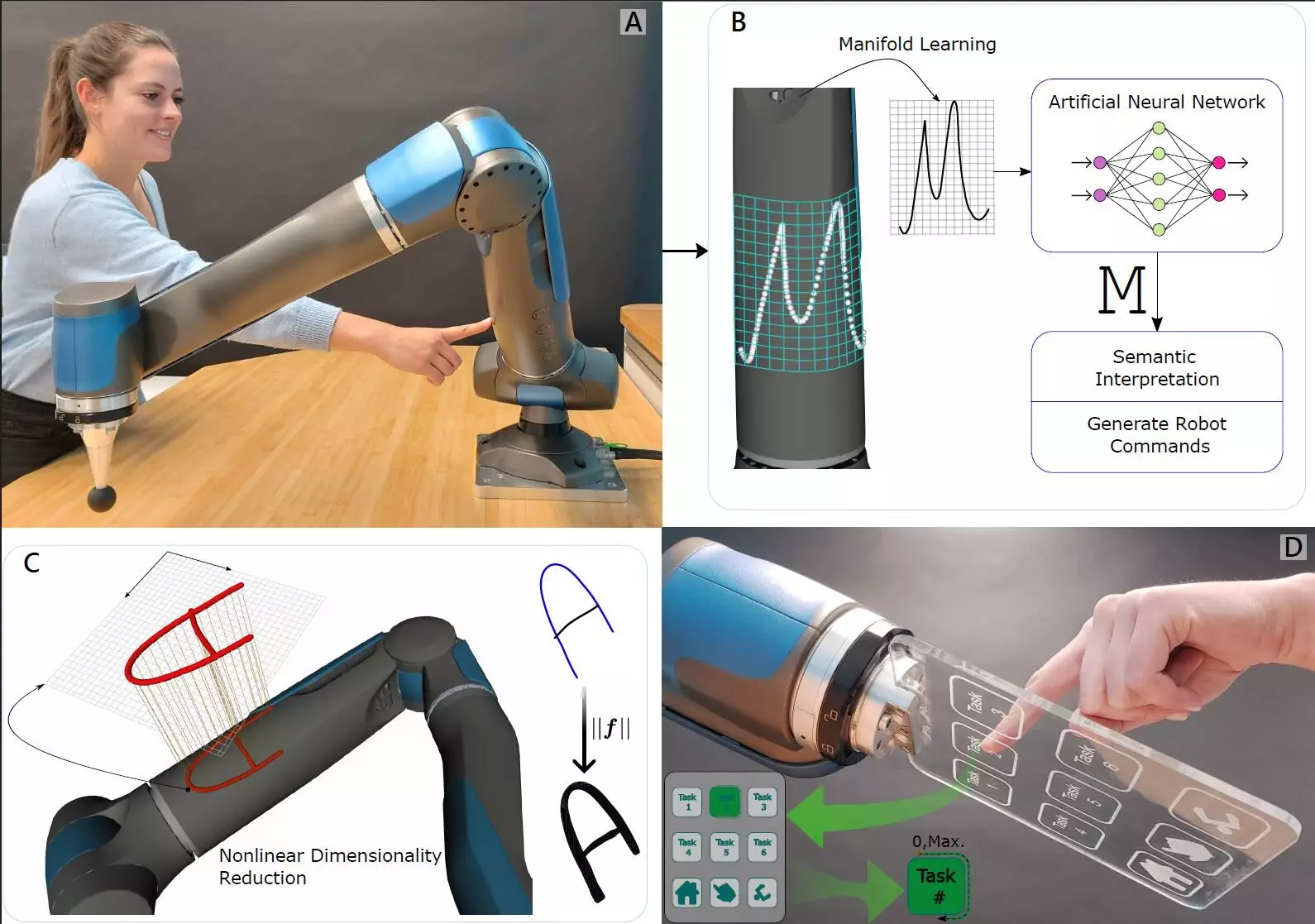
The researchers ingeniously focused on torque, a mechanical phenomenon that governs how forces interact within the joints of a robotic arm. By integrating ultra-sensitive force-torque sensors directly into the joints, the robots became capable of perceiving pressure applied from multiple directions. This innovative setup allows the robot to not only sense when it is being touched but also to discern the nature and intensity of that touch. For instance, this technique empowers robots to pinpoint the exact location on their arm that is being interacted with, thus enhancing their understanding of spatial awareness.
Insights from Machine Learning
Machine learning plays a crucial role in processing the complex data generated by these sensors. The research team implemented algorithms that enable the robot to interpret diverse tension scenarios that arise during interactions. The result is a robotic arm that exhibits an unprecedented level of sensitivity, capable of distinguishing between a person’s fingertip pressing different numbers painted or drawn on its surface. This kind of fine-tuned responsiveness significantly amplifies the ways robots can interact with their surroundings and with human operators, particularly in industrial settings where collaboration is essential.
Implications for Future Robotics
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching. By facilitating human-like tactile sensations, these robots can establish a more intuitive form of communication with their human counterparts. This could revolutionize industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, where robots are increasingly used as collaborative partners. As the field of robotics continues to advance, this innovative blend of mechanical sensors and machine-learning algorithms paves the way for more sophisticated interactions that mirror the touch capabilities of humans, making robots not just tools, but able companions in various environments.

Leave a Reply