Quantum technology is a rapidly advancing field with endless possibilities. Researchers from the Institute for Molecular Science have recently made groundbreaking discoveries in quantum entanglement between electronic and motional states. This has opened up new doors for quantum simulation and quantum computing.
The Power of Quantum Entanglement
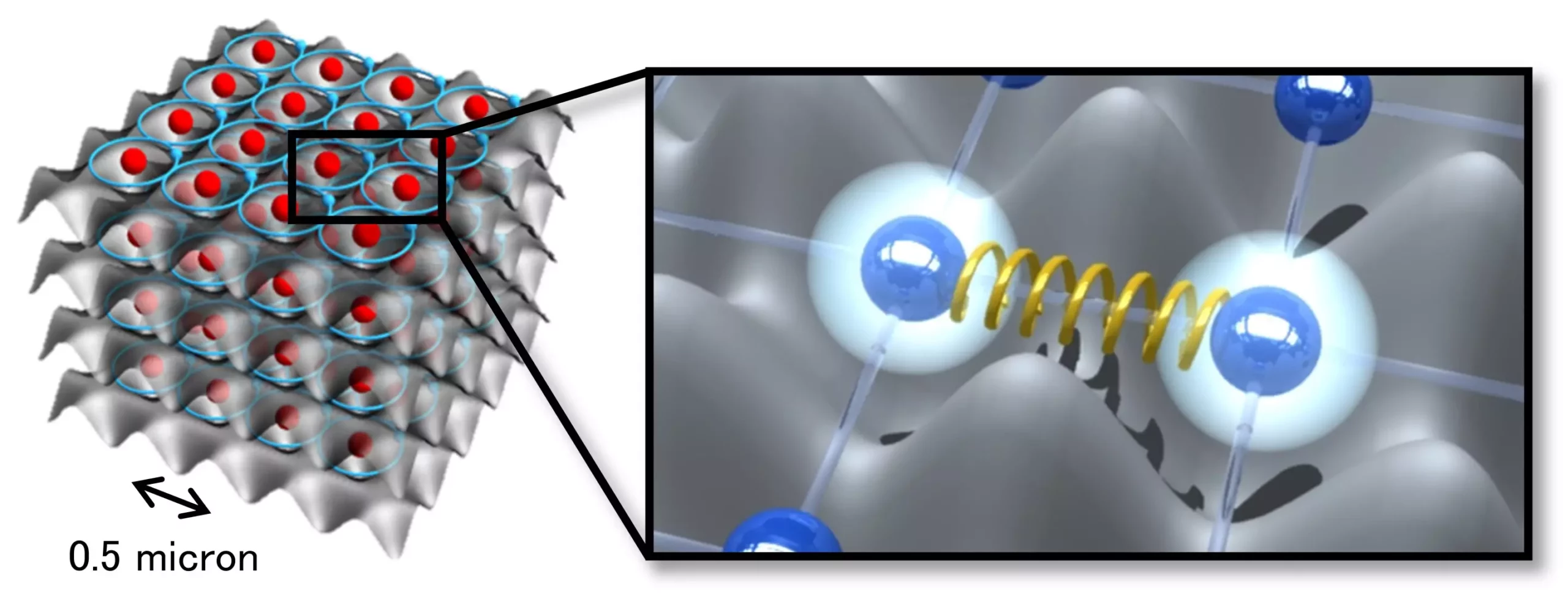
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where particles become correlated and can no longer be described independently. This plays a crucial role in quantum technology, allowing for the development of powerful tools like quantum simulators and quantum computers. In the study conducted by the researchers, they found that the entanglement between electronic and motional states was facilitated by the repulsive force between Rydberg atoms.
Ultrafast Quantum Simulators
The researchers at the Institute for Molecular Science used ultrafast quantum simulators to explore these quantum entanglement phenomena. By cooling down Rubidium atoms to 100 nanokelvin and loading them into an optical trap, they were able to create a quantum superposition between the ground state and the Rydberg state using a pulse laser. This allowed them to observe the formation of entanglement in just a few nanoseconds.
One of the challenges in previous studies was the restriction of the distance between Rydberg atoms due to the Rydberg blockade effect. However, the researchers were able to overcome this limitation by employing ultrafast excitation methods with pulse lasers. This breakthrough enabled them to observe the entanglement between electronic and motional states, which was previously difficult to achieve.
Proposed Quantum Simulation Method
In addition to their experimental findings, the researchers also proposed a new quantum simulation method that involves introducing a repulsive force between particles. By exciting atoms in Rydberg states on a nanosecond scale, they were able to control the repulsive force between atoms trapped in an optical lattice. This innovative approach is expected to revolutionize quantum simulations involving motional states of particles.
The research group is also focusing on developing an ultrafast cold-atom quantum computer that can accelerate two-qubit gate operations significantly. By utilizing Rydberg states and understanding the effects of atomic motion during interactions, they aim to enhance the fidelity of quantum operations. This progress is a crucial step towards realizing efficient and socially beneficial quantum computers in the future.
The study conducted by the researchers from the Institute for Molecular Science sheds light on the exciting future of quantum technology. By leveraging quantum entanglement between electronic and motional states, they have paved the way for new quantum simulation methods and advancements in quantum computing. The potential applications of this research are vast, promising a future where quantum technology transforms industries and societies.

Leave a Reply