The demand for wireless internet access is at an all-time high, with more and more people relying on it for their daily activities. However, this increased demand also leads to higher power consumption and carbon emissions. In order to address this issue, researchers have been developing energy-efficient techniques to support communication between devices and the sharing of information online. One such solution is visible light communication (VLC), which utilizes visible light to transmit data.
Researchers at Central University (CU), IIDM and CU J&K in India have recently developed a new hybrid approach that merges VLC with RF communication. This hybrid solution, as outlined in a paper published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, aims to enable reliable communication in indoor environments with a high data transmission rate, while consuming less energy. The team behind this approach includes Haneet Kour, Rakesh Kumar Jha, and Sanjeev Jain.
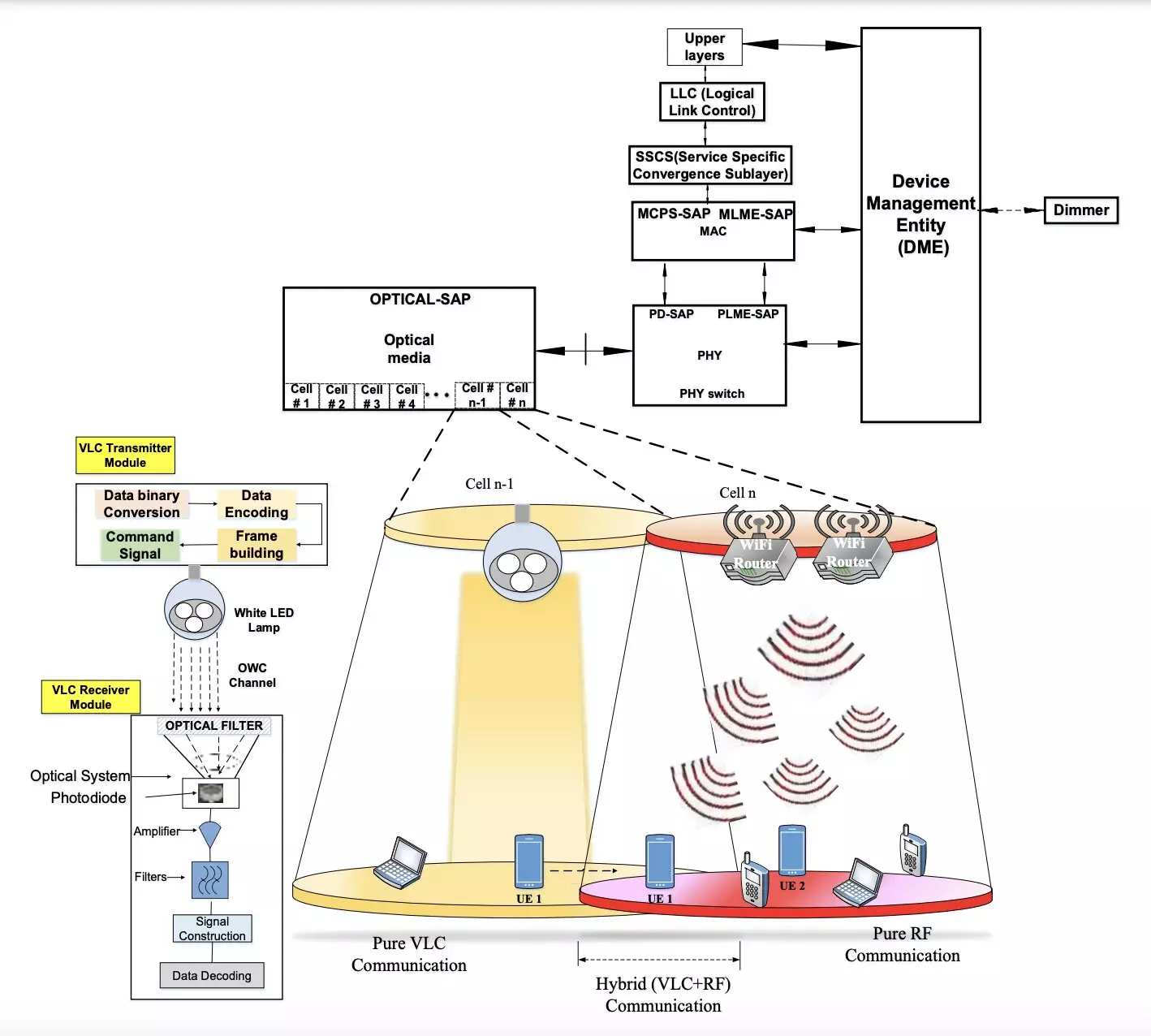
The wireless communication system devised by the researchers consists of two key components: a transmitter and a receiver module. The transmitter, as the name suggests, transmits binary data using LED-produced light. On the other hand, the receiver is equipped with a photo-sensitive device, such as a photodiode or a camera, to extract the transmitted information from the light emitted by the transmitter.
The team conducted an initial evaluation of their proposed system using various simulation platforms. The results indicate that the system could facilitate stable communication in indoor environments while achieving significant energy savings. The researchers compared their hybrid approach with traditional RF communication and pure VLC, demonstrating high energy efficiency and improved battery lifetime for mobile devices.
The study conducted by the researchers from Central University, IIDM, and CU J&K contributes to the ongoing efforts to enhance the energy efficiency of wireless communications. Their hybrid approach shows promise in reducing power consumption and electromagnetic radiation, showcasing the potential for further development and testing in future studies. By merging VLC with RF communication, the researchers have paved the way for a more sustainable future for wireless communication technologies.

Leave a Reply