Recent studies have shed light on the potential impact of global warming on the Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current (AMOC) and its implications for the climate in Northern Europe. Despite the region’s current relatively warm climate, there is growing concern that this warmth could disappear by the turn of the century if the AMOC were to cease running. This major ocean current plays a crucial role in carrying warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to the north Atlantic, where it cools, sinks, and releases heat that keeps northern European ports ice-free. However, under the influence of global warming, the AMOC faces challenges that could lead to a significant disruption in its circulation patterns.
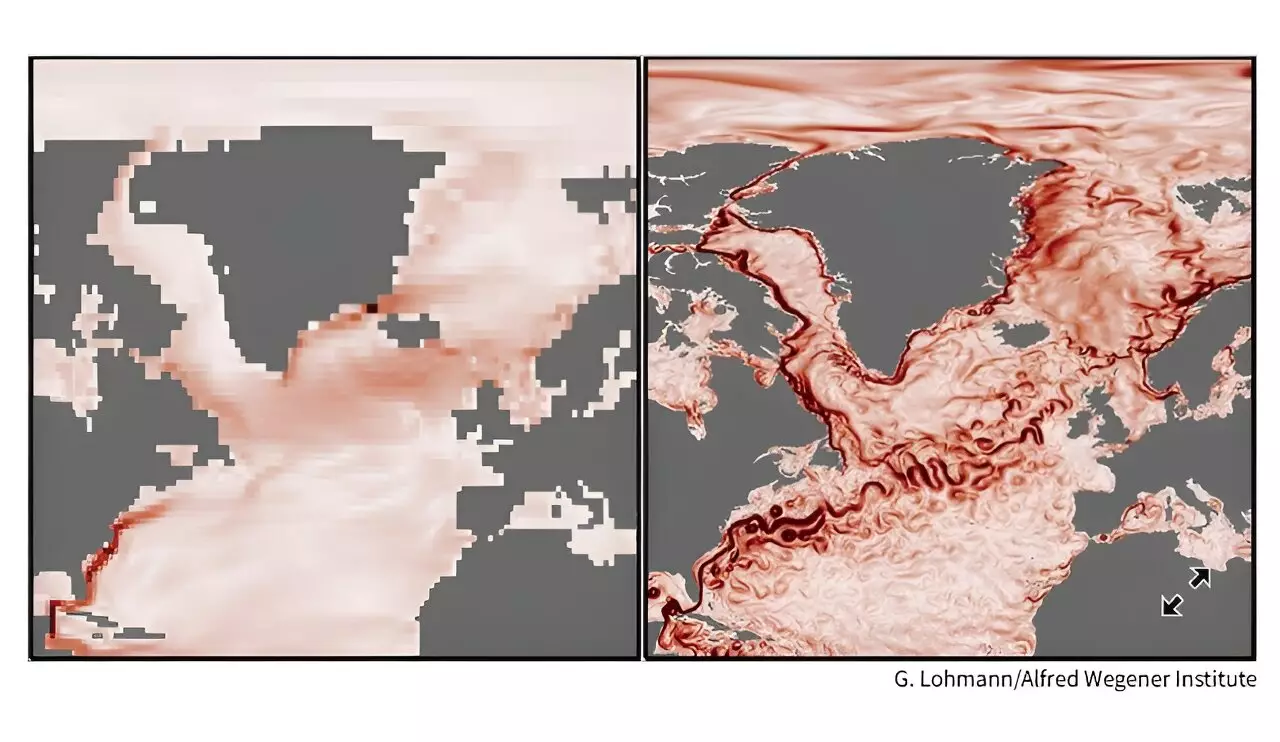
Traditional global climate models have provided valuable insights into the potential impacts of climate change. However, these models are often limited by their low resolution, which can overlook important physical features such as ocean eddies and gyres. The use of a high-resolution climate model called the Community Earth System Model has allowed scientists to delve deeper into the dynamics of the AMOC and its response to extreme greenhouse gas emissions scenarios. By refining the grid sizes and incorporating detailed regional dynamics, researchers have identified previously unknown tipping points and regional variations in the AMOC’s circulation patterns.
Contrary to previous projections, the latest findings suggest a more nuanced picture of the AMOC’s future. While overall trends indicate a slowdown in the AMOC’s circulation, there are unexpected regional variations where parts of the current have collapsed abruptly while others have strengthened over time. These findings challenge the conventional belief that the AMOC is uniformly weakening and emphasize the need to consider localized shifts in climate models to better anticipate and respond to changes in the planet’s systems. Furthermore, the interactions between the overall AMOC and its smaller-scale components raise questions about the future dynamics of this vital ocean current system.
As we confront an uncertain climatic future, the insights gained from the latest climate models underscore the critical importance of advancing our understanding of complex systems like the AMOC. By incorporating regional dynamics and tipping points into our forecasts, we can better prepare for the potential impacts of climate change on our planet’s climate and marine ecosystems. The urgent need to address these challenges highlights the importance of ongoing research efforts to enhance our ability to predict and adapt to dramatic changes in the Earth’s climate system.
The evolving research on the AMOC offers valuable insights into the complexities of our planet’s climate system and the need for more sophisticated climate models. By reevaluating our approach to understanding and forecasting the impacts of global warming, we can take proactive steps towards building climate resilience and mitigating the risks associated with climate change.

Leave a Reply